

Lawyers scheduling the appearance of witnesses for court testimony, and managers scheduling a list of speakers at a conference, take advantage of these effects when they put speakers they wish to emphasize at the very beginning or the very end of a long list.
#Serial position effect serial#
Taken together the primacy effect and the recency effect predict that, in a list of items, the ones most likely to be remembered are the items near the beginning and the end of the list ( serial position effect). The recency effect is comparable to the primacy effect, but for final stimuli or observations. The phenomenon is said to be due to the fact that the short term memory at the beginning of whatever sequence of events is being presented, is far less 'crowded' and that since there are far fewer items being processed in the brain at the time when presented than later, there is more time for rehearsal or pondering of the stimuli which can cause them to be 'transferred' to the long term memory for longer storage. If, for example, a subject reads a sufficiently long list of words, he or she is more likely to remember words read toward the beginning than words read in the middle. The primacy effect, in psychology and sociology, is a cognitive bias that results from disproportionate salience of initial stimuli or observations. Primacy effect Main article: Primacy effect
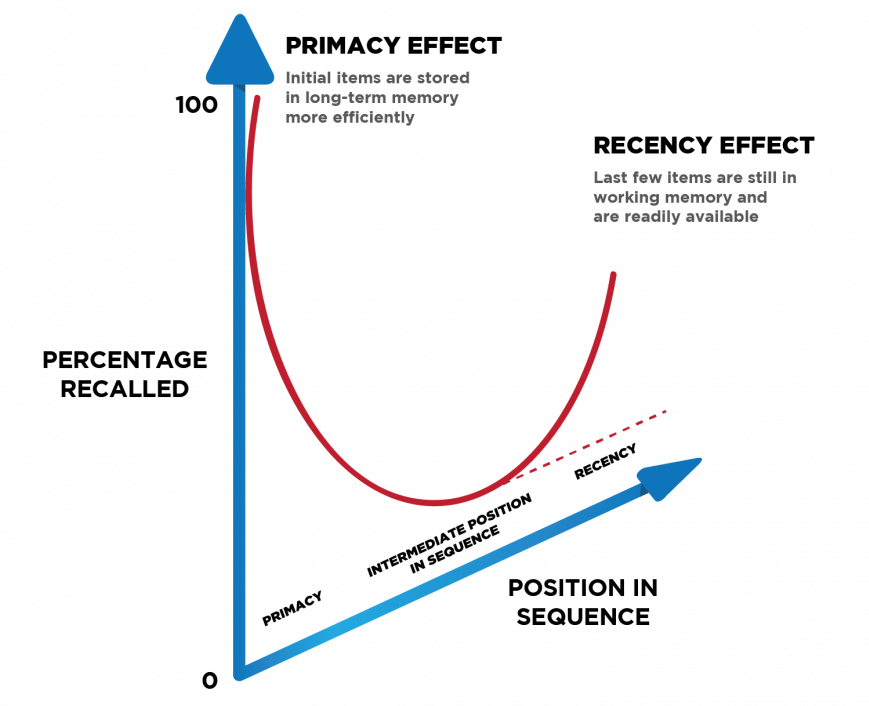
One suggested reason for the primacy effect is that the initial items presented are most effectively stored in long-term memory because of the greater amount of processing devoted to them.
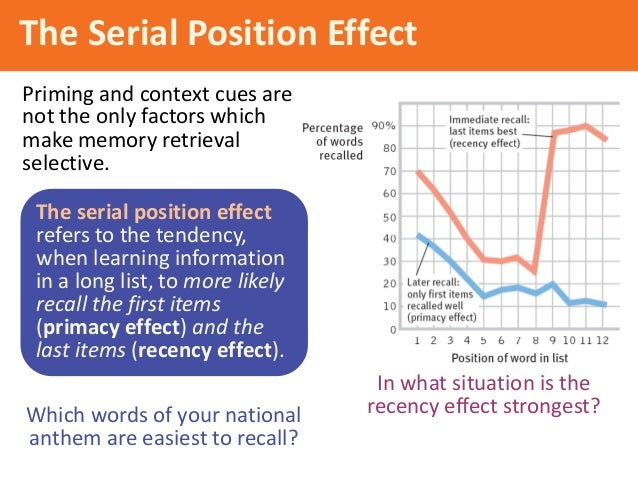
Among earlier list items, the first few items are recalled more frequently than the middle items (the primacy effect). When asked to recall a list of items in any order (free recall), people tend to begin recall with the end of the list, recalling those items best (the recency effect). The serial position effect refers to the finding that recall accuracy varies as a function of an item's position within a study list. Graph showing the serial position effect, the vertical axis shows the percentage of words recalled, the horizontal axis shows their position in the sequence


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
